Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation on 11/16/2017 in all areas
-
Смаунтить диски в другой системе, поискать файл group и поправить его. /etc/group -- это ASCII-файл, описывающий группы, к которым принадлежат пользователи. В нем находятся однострочные записи в формате group_name:passwd:GID:user_list для примера можно посмотреть на другой сино какие там записи и как они правильно выглядят. Либо тоже смаунтить диски и попробовать сделать chroot и уже из системы включить ssh: т.е. обычно порядок такой: загрузился в убунту, сделал маунт proc, sysfs и dev, потом винты, и потом делаешь chroot в папку + указывают путь до bash. Все, ты в своей сино с её окружением. Находишь конфиг ssh правишь его, и добавляешь в автозапуск.2 points
-
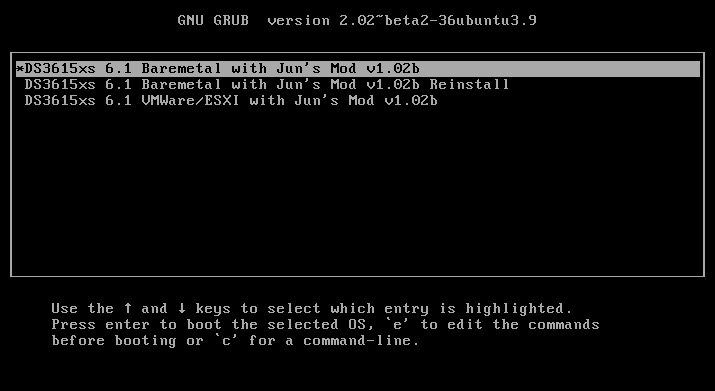
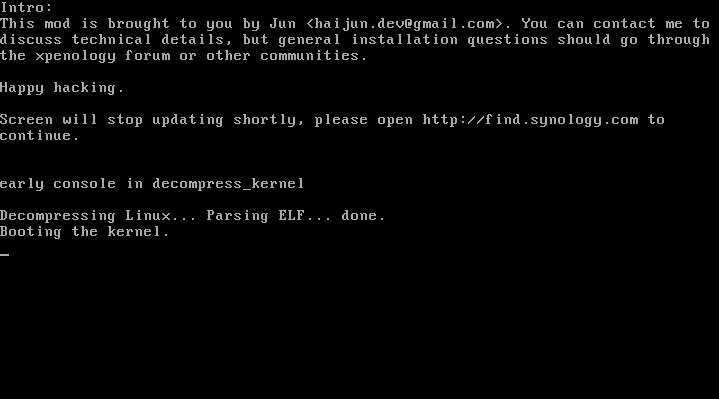
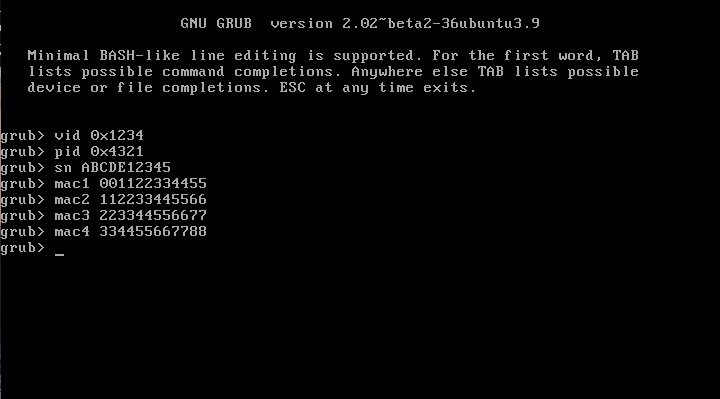
This is an updated tutorial version from the one I made last year. It will enable you to migrate from DSM 5.2 to DSM 6.1.7 directly without the need to upgrade to DSM 6.0.2 first. If for some reason you want to upgrade to DSM 6.0.2 first or simply you do not want to upgrade to DSM 6.1.7 but only to DSM 6.0.2 then use the link above. To upgrade from DSM 6.0.2 to DSM 6.1.7 read here. As most of you know by now Jun was able to find a way to install DSM 6 on non Synology boxes. Here is the thread that I recommend reading. At least make an effort and read the OP: https://xpenology.com/forum/topic/6253-dsm-6xx-loader/ Below is what you need for the operation. I will assume you are doing all this under Windows 10, 8, 7 or XP. If you are on a MAC computer have a look at this post I made on how to burn the image to a USB drive and then mounting the USB drive for editing the content. The rest of the tutorial still applies. If you are currently using DSM 5.1 or below first update to DSM 5.2. If you are doing a fresh install of DSM 6.1 then carry on with the tutorial and omit references to DSM 5.2. - Win32 Disk Imager to make a bootable USB drive; - A 4GB (or any size really) USB drive (flash drive) to install the loader. Not that this is necessary but use preferably a brand name (Kingston, SanDisk...); - A way to read your USB drive VID/PID. Here is a how-to >>> VID and PID; - A good text editor: Notepad++ I really don't recommend using Windows's Notepad; - DSM 6.1.7 PAT file. Chose the one you need: DS3615sx or DS3617sx or DS916+. Download the ".pat" file not the ".pat.md5" - Jun's official v1.02b loader (mirror). This is a hybrid UEFI/BIOS loader so it should work in most machines which are capable or reading GUID partition table (GPT). For older machines that can only read MBR the above loader will simply not boot. If that is your case then use @Genesys's v1.02b loader rebuilt image which is MBR based. Note: Jun's loader supports Intel CPUs. For AMD CPUs Jun has stated that the loader needs some work but it has been reported by many users using HP machines that it actually works. The C1E function in the bios (in some HP machines) needs to be deactivated. I am unsure for other motherboards brands therefore if you have an AMD machine that is not an HP you might be out of luck. Try looking in the bios configuration and play around. - Custom extra.lzma ramdisk. This ramdisk is optional and should only be used if the default ramdisk included in the loader is not detecting your hardware. I am just providing it for those who are having issues with network detection or unrecognised HDD controllers. This custom ramdisk contains additional and updated modules & firmwares. Credits go to @IG-88 for compiling the modules against the latest DSM 6.1.3 source code. I do not warranty they all work but I think most do. If you chose to use this ramdisk, you will need to replace (or rename, so you can revert) the default extra.lzma ramdisk from Jun's loader with this one. If you a have question specific to the custom ramdisk please post it in the topic of IG-88, not here. - If you are doing a fresh install make sure your drives are plugged in direct succession starting from the 1st SATA port. Usually the first port is described as SATA0 on motherboards. Check with your MoBo manufacturer for exact nomenclature. - OSFMount to modify the grub.cfg file within the loader's image and if necessary to replace the extra.lzma ramdisk with the custom one. This is not strictly necessary as Jun has made it possible to configure what needs to be modified via the Grub Boot Menu. If you prefer using Jun's Grub Boot Menu configuration method, simply skip Point 4, read Note 4 instead and pick up at Point 5. PLEASE READ EVERYTHING PRIOR ATTEMPTING ANYTHING Use this loader at your own risk. I wont be held responsible for any loss of data or black smokes that may result in the use of this loader. Please note that this loader has a limited amount of modules (drivers) included. If it is fundamental for you to have a NAS operating as quick as possible I recommend you look at the included drivers very carefully at the bottom of this tutorial before attempting an upgrade. If they are not there you will have to compile your own modules/firmwares or use the custom ramdisk provided above. Don't ask me to compile modules for you. I wont do it. One last thing: DO NOT UPDATE DSM BEYOND VERSION 6.1.7 with loader v1.02b. IN OTHER WORDS DO NOT UPDATE TO DSM 6.2 You have been warned. Here we go: 1 - BACKUP your data and save your configuration prior any attempts to migrate from DMS 5.2 to DSM 6.1. I can't stress this enough. JUST DO IT, as Nike likes to say. Also, print this tutorial if you can. It will make your life easier. 2 - Turn off your NAS and unplug the USB drive you are currently using with DSM 5.2. I recommend you put this USB drive aside in case migration to DSM 6.1 doesn’t go as expected and you need to revert to DSM 5.2. It will just make your life easier. 3 - Now go to your workstation/PC, plug a new USB drive (or the old one if you really don’t have any spare USB drives). Use the link I provided earlier to check your USB drive VID/PID. Write down the info somewhere as we will need it later. 4 - Now launch OSFMount. Select Mount New, then select the image file you downloaded earlier (i.e. .img extension file) to open. Now select partition 0 (the one that is 15 MB). Click Ok. Then at the bottom of the window make sure to un-tick the "Read only drive". Click Ok. The partition should now be mounted in file explorer. At this point you can navigate to the /grub directory and edit the grub.cfg file. If you need to replace the extra.lzma ramdisk with the custom ramdisk provided above then you will also need to mount partition 1 (the one that is 30 MB). Below is what you will see in the grub.cfg file. I am only showing below the portion of the code that is relevant for the purpose of this tutorial [...] set extra_initrd="extra.lzma" set info="info.txt" set vid=0x058f set pid=0x6387 set sn=C7LWN09761 set mac1=0011322CA785 set rootdev=/dev/md0 set netif_num=1 set extra_args_3615='' set common_args_3615='syno_hdd_powerup_seq=0 HddHotplug=0 syno_hw_version=DS3615xs vender_format_version=2 console=ttyS0,115200n8 withefi elevator=elevator quiet' set sata_args='sata_uid=1 sata_pcislot=5 synoboot_satadom=1 DiskIdxMap=0C SataPortMap=1 SasIdxMap=0' set default='0' set timeout='1' set fallback='1' [...] You want to modify the following: Change vid=0x090C to vid=0x[your usb drive vid] Change pid=0x1000 to pid=0x[your usb drive pid] Change sn=C7LWN09761 to sn=generate your sn here with DS3615xs or DS 3617xs or DS916+ model (this will depend on which loader you chose) Change mac1=0011322CA785 to mac1=[your NIC MAC address #1]. You can also add set mac2=[your NIC MAC address #2] and so on until mac4 if you have multiple NICs. However, this is not necessary. Recommended: Change set timeout='1' to set timeout='4' - This will allow you more time to make a selection in the Grub Boot Menu when it appears on screen. Once you are done editing the grub.cfg file, save it and close your text editor. Now in OSFMount click on Dismount all & Exit. You are now ready to burn the image to your USB drive. 5 - Now use Win32 Disk Imager to burn the image file onto the USB drive. This will also make the USB drive bootable. 6 - Eject and unplug the USB drive from your workstation. Plug it in your NAS (avoid USB 3.0 ports. Use USB 2.0 port if available). Boot your NAS and before doing anything fancy, access your BIOS so to make your USB drive the 1st boot drive if it's not the case. The Jun official loader can boot in UEFI or in legacy BIOS, so you chose what suits you best. Also, make sure your HDDs are booting in AHCI mode and not in IDE. Finally, if disabled, also enable the serial port in BIOS. Some BIOS don't have this option so don't get too cranky on this if you can't find it. Save changes to the BIOS and REBOOT the NAS. 7 - Once rebooted, if you have a monitor connected to your NAS you will see the following Grub Boot Menu: ADVICE: even before you see the Grub Boot Menu press the up/down key. This will stop the countdown so you will be able to select the desired line. You won’t see much other than the following after you press enter: If you booted the USB drive in EFI mode then you will see the same text without the last 3 lines but that's ok. 8 - Now go back to your workstation, and launch Synology Assitant or go to http://find.synology.com. Within one minute or so you should normally be able to see your NAS on your local network (it took ~55 seconds on a test I did on a VM). Just follow the instructions and either chose "Install" if you wish to have a clean install or chose “Migration” if you are coming from DMS 5.2 and wish to update while retaining your data. You will be asked to provide the .PAT file you downloaded earlier (DSM_DS3615xs_15217.pat or DSM_DS3617xs_15217.pat or DSM_DS916+_15217.pat). 9 - When the migration is finished you will most probably have to update some of your packages. You can then proceed and update DSM 6.1.7 up to DSM 6.1.7 critical update 3. It is possible you might either need to hard reboot or re-image your usb drive. Make sure to deactivate auto-updates within DSM. Link to individual files (DSM and critical updates) can be found here: https://xpenology.com/forum/topic/7294-links-to-dsm-and-critical-updates/. DO NOT UPDATE TO DSM 6.2. The loader is not compatible. 10 - You are done. If you have questions, first search the forum and/or Google then leave a comment if nothing helps. Please provide your hardware specifications (motherboard model, LAN controller, driver controller etc). Failure to prove such information will lead to the post being deleted or not answered. -------------- Note 1: If after following the tutorial you can’t find your NAS through http://find.synology.com ou Synology Assistant it is highly possible that the drivers of your NIC are not included in the ramdisk of the loader. Make an effort and use Google to know what modules your NIC and HDD controller are using, then check if those modules are included in the custom extra.lzma ramdisk. If yes then use the custom ramdisk. Don't ask me to look for you. If nothing works then ask your question. Note 2: Synology increased security since the introduction of DSM 6. Root access through SSH is no longer possible out of the box. You can however use your admin account and elevate permissions with the following command if you need root permissions: sudo -i Note 3: Please check you have the right VID/PID prior proceeding. If you get the following error ”Failed to install the file. The file is probably corrupted. (13)" it most certainly means your VID and/or PID is/are wrong. If you still have the same error message after verifying the VID/PID then try another USB drive. Note 4: Configuration added to the grub.cfg file can also be done directly during the Grub Boot Menu, so technically you can skip Point 4 and burn the image on the USB drive without editing anything (read Point 5 onward first). If you wish to do the changes from the Grub Boot Menu directly you need to press the letter 'C' when you see the Boot Menu. You will literally only have one second, so be fast. Once you press 'C' you will be in a Grub command line environment. To change your VID enter the following: vid 0xYOUR 4 DIGITS USB DRIVE VID Do the same for pid, sn and mac1. Press enter at each command. The commands are: pid 0xYOUR 4 DIGITS USB DRIVE PID sn YOUR NAS SERIAL NUMBER mac1 YOUR NAS MAC1 ADDRESS If you have multiple NICs you can also issue mac2, mac3 and mac4 as commands. Maximum is mac4. See below: mac2 YOUR NAS MAC2 ADDRESS mac3 YOUR NAS MAC3 ADDRESS mac4 YOUR NAS MAC4 ADDRESS If you think you made a mistake in the numbers simply re-issue the command. When you are done press esc and select the appropriate menu entry. Below is an example (fake numbers) of how it looks under the Grub command line environment : Note 5: If you encounter the error "We've detected errors on your hard drives [drive number] and the SATA ports have also been disabled" during installation, then you have to fallback to adding SataPortMap to the grub environment. Press the letter 'C' at the Grub Boot Menu and then add the following: append SataPortMap=XX where XX is the number of drives. Don’t forget to update this parameter if you add additional drives to your machine. If you use Reinstall, don't forget to re-select the first line of the Boot Menu once the NAS has rebooted after the installation else the Loader will re-select Reinstall and you will be faced with some issues so please beware of this. @@@@@@@@ What does SataPortMap mean? @@@@@@@ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ ############## Know issues ##################### - When running on a slow single core machine, there is a race condition that causes the patcher to load too late. The most obvious sign is that console is not working properly. - Some ethernet drivers crash when set MTU above about 4096 (Jumbo frame). ############# Included default modules & firmwares in Jun's Loader ############# ############## Tutorial UPDATES ##################1 point
-
Hi, Thanks to Aigor and IG-88 i managed to compile drivers in Bash for windows. I used snippets from both users to make this tutorial! Thanks for that! Follow the tutor here: http://xpenology.club/compile-drivers-x ... d-in-bash/1 point
-
REMEMBER TO BACKUP BEFORE MESSING WITH DISKS OR PARTITIONS/VOLUMES Tested on DSM 6.1 through ESXI 6 here. Few days ago, my DSM started complaining about low disk space available on volume 1. It was only 16gb. So, i tried to expand it few times after expanding .vmdk but "Extend" buttond stay grayed. After few tries and installations f*cked up, here is the way i did it, and it should work on barebone install too : Keep the disk you want to "copy" in the Diskstation, then put the new drive in avalible slot, and make them to RAID1 - mirror. When the its done, then remove old volume 1 disk and add change freshly added disk to whatever was ancient volume 1 (i.e scsi 0:0, or 0:1). This will give you a degraded state Raid 1 with only new volume 1. Then activate Telnet an use this command : mdadm --grow --raid-devices=1 --force /dev/md2 (RAID1 to BASIC) Now the new disk is basic again an you can expand it to its full size.1 point
-
восстанови с сохранением данных ! данные софта тоже останутся когда их поставишь !1 point
-
Я бы Вам предложил запустить его в docker. Когда поставите docker, поищите linuxserver/transmission. Настройки там минимальные, смотрите на скриншотах. Отличный, разжеванный вариант есть у Bob the Builder, он его использовал в связке с Torrenmontor для автоматического слежения за обновлением торрент-файлов на раздачах.1 point
-
Hey again, I do think I found the issue from the log (disk_log.xml for future reference). This was the first try on 2017-10-01 when I tried expanding the array: <kernel time="2017/10/01 03:58:04" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="590338" show="0">RecovComm Persist PHYRdyChg 10B8B </ker nel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 04:18:48" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 04:39:55" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugout</hotplug> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 04:39:55" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugin</hotplug> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 05:01:59" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugout</hotplug> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 05:01:59" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugin</hotplug> <kernel time="2017/10/01 05:31:08" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66050" show="0">RecovComm Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 05:52:41" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 06:13:44" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 06:36:21" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 06:57:24" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 07:18:03" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 07:39:06" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 07:59:42" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 08:20:22" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 08:41:23" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugout</hotplug> <hotplug time="2017/10/01 08:41:23" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugin</hotplug> <kernel time="2017/10/01 09:02:25" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66050" show="0">RecovComm Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 09:23:28" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 09:44:07" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 10:06:22" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/10/01 10:27:25" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> And the second time on 2017-11-12: <kernel time="2017/11/12 03:50:24" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="590338" show="0">RecovComm Persist PHYRdyChg 10B8B </ker nel> <hotplug time="2017/11/12 04:11:05" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugout</hotplug> <hotplug time="2017/11/12 04:11:05" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" show="1">plugin</hotplug> <kernel time="2017/11/12 04:32:05" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66050" show="0">RecovComm Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 05:06:43" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 05:27:45" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 05:48:49" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 06:09:25" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 06:30:13" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 06:56:13" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 07:17:42" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 07:38:44" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 08:00:24" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 08:34:54" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 08:55:56" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 09:16:37" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 09:38:24" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 09:59:00" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 10:19:43" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 10:40:28" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> <kernel time="2017/11/12 11:02:24" path="/dev/sde" model="WD30EFRX-68EUZN0" SN="WD-WMC4N1830023" type="serror" raw="66048" show="0">Persist PHYRdyChg </kernel> The same issue repeated, but without the several "plugout/plugin" events. After this revelation I found some reference from the unRaid wiki. So it seems that the PHYRdyChg / 10B8B-errors are most probably due to bad connections from either the SATA-cable or the SATA power cable. The difference between the two tries was that I changed the SATA-cable to another one and I didn't get any CRC-errors on either time. This leads me to the SATA power cable/plug or HD connector. I didn't change the power cable between the two tries. There is two other possibilities still, namely too many hard drives on one lead/rail (although the WD Red was closest to the PSU). I also had HD hibernation on from DSM, which could mimic the hotplug events if the drive doesn't spool up fast enough etc. This could well be the culprit here, since the drive was ok until the expansion / repair was done, which took several hours both times. So according to this research: Faulty SATA cable (changed, no difference) Faulty SATA power cable / plug (to be tested) Faulty SATA connector on drive (visual inspection ok) Too many drives on one lead / rail Software issue with WD Red drives and hibernation For now I've disabled HD hibernation and I'll plug the drive to another slot / cable and proceed with the repair. I'll report back after the server has run the repair overnight. Janne1 point
-
1 point
-
у меня не Gigabyte а ASRock N3150DC-ITX, но это не принципиально вообще-то, System-on-Chip (SoC) одна и таже в конце августа тоже переехал с dsm5.2 3615xs на dsm6.1.3 и уже на 916+, которая по железу как раз подходит и здесь стоит отметить что у меня установлена дополнительная сетевая Intel PRO/1000 PT Server, это может быть важно потаму как если помотреть лог ядра то там светится толька эта карта, хотя сразу говорю что в dsm светятся обе карты, вот кусок лога где все дрова для сетевых карт, где 00:15:17:97:8c:67 - мак дополнительной карты модуль r8168 Realtek тоже присутствует но мака от карты нет, я не знаю но может это такая особенность и различие интеловких и реалтэковых сетевых kern.log 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.402912] e1000e: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Driver - 3.3.4-NAPI 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.402919] e1000e: Copyright(c) 1999 - 2016 Intel Corporation. 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.403234] e1000e 0000:01:00.0: Interrupt Throttling Rate (ints/sec) set to dynamic conservative mode 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.403289] e1000e 0000:01:00.0: irq 138 for MSI/MSI-X 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.579365] e1000e 0000:01:00.0 eth0: (PCI Express:2.5GT/s:Width x1) 00:15:17:97:8c:67 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.579373] e1000e 0000:01:00.0 eth0: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Connection 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.579457] e1000e 0000:01:00.0 eth0: MAC: 1, PHY: 4, PBA No: D50861-003 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.617448] ixgbe: Unknown symbol mdio_mii_ioctl (err 0) 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.617502] ixgbe: Unknown symbol mdio45_probe (err 0) 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.652530] r8168 Copyright (C) 2017 Realtek NIC software team <nicfae@realtek.com> 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.652530] This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details, please see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. 2017-08-27T06:13:11-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 42.652530] This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions; see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. 2017-08-27T06:13:12-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.266913] e1000: Intel(R) PRO/1000 Network Driver - version 7.3.21-k8-NAPI 2017-08-27T06:13:12-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.266920] e1000: Copyright (c) 1999-2006 Intel Corporation. 2017-08-27T06:13:12-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.328975] ixgbe: Intel(R) 10 Gigabit PCI Express Network Driver - version 3.13.10-k 2017-08-27T06:13:12-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.328982] ixgbe: Copyright (c) 1999-2013 Intel Corporation. 2017-08-27T06:13:13-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.472794] 2017-8-27 13:13:13 UTC 2017-08-27T06:13:13-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.472814] Brand: Synology 2017-08-27T06:13:13-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.472818] Model: DS-916+ 2017-08-27T06:13:13-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 43.472823] This is default settings: set group disks wakeup number to 1, spinup time deno 1 2017-08-27T06:13:15-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 45.600244] e1000e 0000:01:00.0: irq 138 for MSI/MSI-X 2017-08-27T06:13:15-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 45.700790] e1000e 0000:01:00.0: irq 138 for MSI/MSI-X 2017-08-27T06:13:17-07:00 DiskStation kernel: [ 47.839799] e1000e: eth0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: Rx/Tx Hide1 point
-
1 point
-
Why do you not search on the synology site for a usb drive wjich is compatible? Then the USB drive will automatically power up and down ... Worked for me with a mybook essential for a long time, before I replaced it with my old 411j1 point